As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the need for region-specific regulation of mobile applications becomes increasingly critical. This article delves into the various methods and technologies employed to enforce regional bans on mobile apps, offering insights for both novices and experts in the technology sector. By understanding the intricacies and legalities involved, stakeholders can navigate this complex field more effectively.
The ability to restrict mobile applications within specific geographic boundaries has significant implications for privacy, security, and compliance. Whether driven by government mandates or cultural norms, the techniques for app banning discussed here combine legal frameworks with advanced technology solutions to achieve desired outcomes.
Overview of Regional Bans on Mobile Applications
Regional bans on mobile applications can arise from various motivations including political, legal, and cultural considerations. These bans are implemented to control the digital environment within a specific geographical area, impacting both app developers and users. Understanding the reasons behind these bans is crucial for compliance and operational strategy.
The mechanisms for enforcing these bans involve a coordinated effort between governments, technology providers, and regulatory bodies. They focus on limiting the availability and functionality of certain apps, thus shaping the digital landscape to reflect regional norms and laws.
Legal Frameworks for Application Bans
Legal provisions form the backbone of any regional app ban. Countries typically enact laws that govern digital content, which include specific clauses for mobile applications. These laws not only define the legality of certain content but also prescribe the mechanisms for enforcement and penalties for non-compliance.
In different jurisdictions, the legal process may vary, but common elements include judicial orders, direct government mandates, or regulatory guidelines that target specific types of applications. These frameworks ensure that bans are not arbitrary but are supported by legal justifications that align with broader policy objectives.
Geo-IP Blocking and Its Effectiveness
Geo-IP blocking is a widely used method to enforce regional restrictions on the internet. It works by detecting the geographic location of a user’s IP address and restricting access to certain services accordingly. This method is particularly effective for initial enforcement of regional bans on mobile applications.
However, its effectiveness can be limited by technologies such as VPNs and proxy servers that allow users to mask their real locations. Despite these challenges, Geo-IP blocking remains a fundamental tool in the arsenal of regional app ban strategies.
Utilizing App Store Control for Regional Restrictions
App stores play a crucial role in the distribution of mobile applications and thus are instrumental in enforcing regional bans. By controlling the availability of apps in specific markets, app stores can comply with regional regulations effectively. This method is straightforward and managed through the app store’s administrative backend.

Both major and minor app stores have policies in place that allow for the removal or restriction of apps based on geographic locations. This ensures that only compliant apps are accessible to users in particular regions, reinforcing legal and regulatory frameworks.
Role of Network Providers in Enforcing App Bans
Network providers are key players in the enforcement of app bans. They can block access to specific services at the network level, making it challenging for users to connect to banned applications. This collaboration between technology providers and regulatory bodies is vital for the effective enforcement of regional policies.
By implementing network-level restrictions, providers can directly prevent the downloading or functioning of specific apps, thus supporting governmental and legal efforts to regulate the digital space within their territories.
Using DNS Filtering to Prevent App Access
DNS filtering is another effective technology used to restrict access to unwanted mobile applications. By blocking domain name resolutions for specific services, users are unable to access the corresponding apps. This method is particularly useful for enforcing comprehensive regional bans.
While DNS filtering is robust in preventing access to certain apps, users may circumvent these restrictions using DNS over HTTPS (DoH) technologies. Nonetheless, when combined with other methods, DNS filtering significantly enhances the effectiveness of regional app bans.
Deploying Application Level Gateways (ALGs)
Application Level Gateways (ALGs) function by inspecting the data passing through a network, allowing them to block or restrict specific applications. This sophisticated technology can identify and manage data packets related to restricted apps, enforcing bans effectively at the application level.
ALGs are particularly useful in environments where maintaining control over application traffic is critical. They provide a granular level of control that complements other regional restriction measures, making them an indispensable part of modern network management.
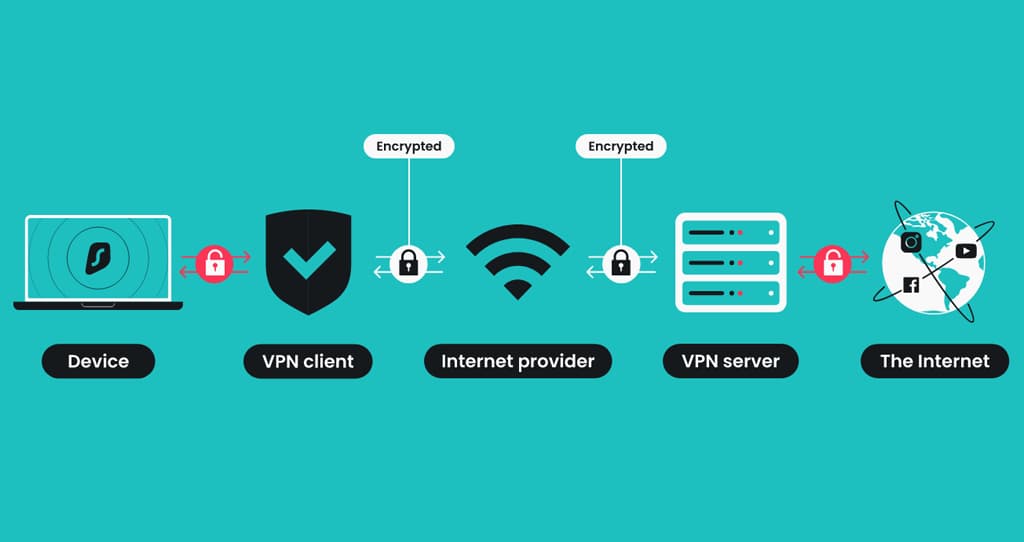
The Importance of VPN Detection Techniques
VPN detection techniques are essential for the effectiveness of regional app bans. These technologies identify and block traffic from Virtual Private Networks, which are often used to bypass geo-restrictions. Effective VPN detection allows for more robust enforcement of regional bans.
While no detection method is foolproof, ongoing advancements in technology are improving the ability to detect and mitigate the use of VPNs for accessing banned applications. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of regional digital policies.
Challenges of Enforcing Regional Bans on Mobile Applications
Enforcing regional bans on mobile applications is fraught with challenges. These range from technological bypasses, such as the use of VPNs, to legal hurdles that involve varying international laws and regulations. Understanding these challenges is key to developing effective enforcement strategies.
Furthermore, the dynamic nature of the digital landscape requires continuous adaptation and updates to enforcement mechanisms. This ensures that they remain effective against new bypass techniques and align with evolving legal standards.
Case Study: Access Betting Apps
A practical example of these challenges and solutions in action is seen in the case of regionally banned betting apps or just if someone want Aviator Game download. These applications are often restricted due to local gambling laws but are also highly sought after by certain user bases, making enforcement particularly difficult.
By employing a combination of Geo-IP blocking, DNS filtering, and active monitoring of network traffic, authorities can significantly reduce unauthorized access. This case study illustrates the multifaceted approach needed to effectively manage app bans in sensitive categories such as gambling.
Monitoring and Compliance: Ensuring the Ban Is Effective
Effective monitoring and compliance systems are essential to ensure that regional bans on mobile applications are adhered to. These systems involve both automated and manual checks to detect any breaches of the enforced bans.
Regular audits and updates to enforcement technologies also play a crucial role in maintaining the efficacy of regional bans. These measures help in adapting to new bypassing methods and ensuring that the intended restrictions are fully operational.
Future Trends in Technology for Regional App Bans
Looking forward, the technology for enforcing regional app bans is likely to evolve with advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies promise to enhance the detection and enforcement capabilities, making regional bans more effective and less intrusive.
Moreover, as digital sovereignty becomes a more prominent issue globally, we can expect more sophisticated and localized approaches to app management and enforcement. These trends will shape the future landscape of digital content control, reflecting the unique needs and regulations of different regions.

Conclusion: The Complexity of Technically Banning Apps
This exploration of the various methods and challenges involved in technically banning mobile applications in specific regions highlights the complexity of the task. Stakeholders must balance technological, legal, and ethical considerations to achieve effective enforcement.
The ongoing development of digital technologies and legal frameworks will continue to influence how regional app bans are implemented. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone involved in the digital ecosystem, ensuring they stay ahead in managing and complying with regional regulations.


